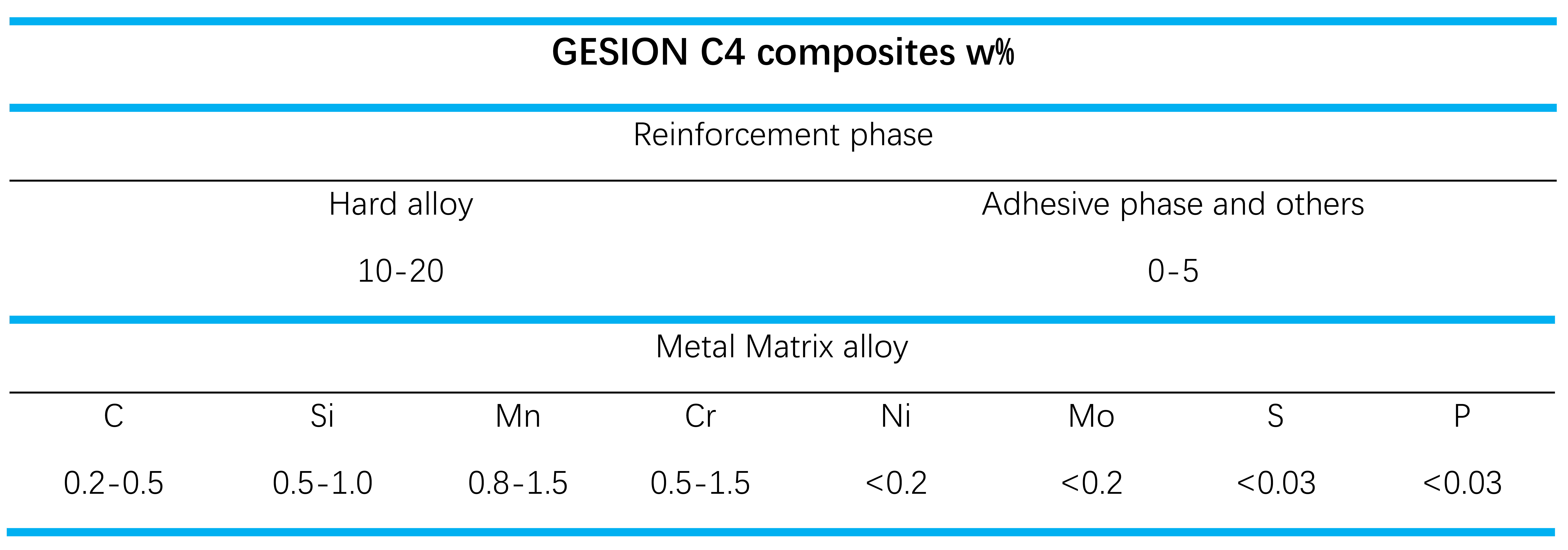
Technical description: There are three main methods of reinforcement for iron-based composite materials: particle reinforcement (zero-dimensional), fiber reinforcement (one-dimensional), and lamellar reinforcement (two-dimensional), as well as network reinforcement (three-dimensional). Three-dimensional continuous reinforcement composites (Co-Continuous Ceramic Composites, abbreviated as C4 materials) feature a three-dimensional network structure where the hard alloy/ceramic reinforcement phase and the metal matrix are interconnected in space. This design allows the material to leverage the high hardness, high strength, and excellent wear resistance of ceramic materials, while also benefiting from the good ductility and toughness of metal materials. Neither the ceramic phase nor the metal phase is isolated in space, exhibiting the positive additive characteristics of both components. Consequently, C4 materials offer significant advantages over one-dimensional and two-dimensional reinforcement materials. Key research points for C4 materials include the preparation of network-intersecting ceramic preforms, methods for controlling the interface formation during composite material molding, improvement of wettability, and infiltration behavior. GESION employs various cutting-edge technologies to obtain continuous reinforcement phases, improve the wettability between the three-dimensional hard phases and the substrate using special processes, and produce continuous reinforcement composites with advanced properties.